A New Light for Chronic Conditions: The Supportive Promise of Expanded Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Supportive Care
A New Light for Chronic Conditions: The Supportive Promise of Expanded Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Expanded Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) safely support chronic conditions, easing symptoms, slowing progression, and improving quality of life.
When a cure isn’t possible, Care and Support still change lives.
Even when a definitive cure is not possible, Expanded Mesenchymal Stem cells (MSCs) offer a scientifically validated, safe, and side-effect–free supportive treatment in a wide range of chronic, degenerative, or treatment-resistant diseases. Their anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, anti-fibrotic, and regenerative properties contribute to improving quality of life, stabilizing symptoms, and slowing disease progression.
Scientifically Supported, Side-Effect-Free supportive uses include:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
MSCs help reduce lung inflammation, improve pulmonary function, and stabilize respiratory symptoms. - Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
While not curative, MSCs may slow neuroinflammation and enhance neurological recovery. - Liver Cirrhosis & Chronic Liver Disease
MSCs reduce fibrosis and improve liver function without adverse effects. - Crohn’s Disease & Ulcerative Colitis (IBD)
Their immunomodulatory effects help control relapses and reduce the need for immunosuppressive drugs. - Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)
MSCs may slow fibrotic progression and improve oxygenation and exercise tolerance.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
MSCs help modulate immune dysfunction and reduce systemic flares. - Spinal Cord Injury (Chronic Phase)
They support neuroprotection and reduce secondary inflammation, promoting limited functional recovery. - Type 1 Diabetes (Early-Stage or Recent-Onset)
MSCs protect pancreatic β-cells and delay autoimmune destruction, although they do not reverse established diabetes. - Heart Failure (Ischemic and Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy)
MSCs can improve cardiac function and reduce inflammatory remodeling of heart tissue.
Even in cases where chronic or degenerative conditions are not curable, expanded Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) can offer powerful supportive benefits—without the side effects of conventional treatments. Thanks to their anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, immunomodulatory, and regenerative actions, MSCs can improve quality of life, reduce symptom severity, and slow the progression of disease. Most importantly, their excellent safety profile has been validated in multiple clinical tria
Supporting Studies - Key References
| Condition | What MSCs Can Do Supportive Benefits |
Supporting Studies Key References |
|---|---|---|
| COPD | Improve lung function and reduce inflammation | Weiss et al., Chest, 2013 [PMID: 23681064] |
| Multiple Sclerosis | Modulate immune response, reduce relapse rate | Llufriu et al., J Transl Med, 2014 [PMID: 24885658] |
| Liver Cirrhosis | Improve liver function, reduce fibrotic damage | Lin et al., Stem Cell Res Ther, 2011 [PMID: 21232138] |
| Crohn’s Disease | Heal fistulas, reduce dependency on drugs | Panés et al., Lancet, 2016 [PMID: 26947890] |
| Pulmonary Fibrosis | Slow fibrotic progression, support oxygenation | Tzouvelekis et al., Chest, 2013 [PMID: 23732584] |
| Systemic Lupus (SLE) | Reduce flares and systemic inflammation | Wang et al., Arthritis Res Ther, 2014 [PMID: 25243800] |
| Spinal Cord Injury | Support limited motor recovery, reduce scarring | Vaquero et al., Cytotherapy, 2016 [PMID: 26921693] |
| Type 1 Diabetes (early stage) | Protect insulin-producing cells | Carlsson et al., Diabetes Care, 2015 [PMID: 26216877] |
| Heart Failure | Improve cardiac output and tissue repair | Bartolucci et al., JACC, 2017 [PMID: 28545673] |
Why choose MSCs for Supportive Care?
- Backed by dozens of human trials with excellent safety profiles
- Allogeneic use approved in many studies, Safe for both autologous and allogeneic use – no HLA matching or immunosuppressants needed
- No teratoma formation and no systemic side effects – Non-immunogenic and non-tumorigenic
- Complementary to standard therapies (e.g., immunosuppressants, DMARDs, steroids), Can be used alongside conventional therapie
- No long-term adverse effectstissue.
Expanded Mesenchymal Stem Cells are Supportive - and Stromal Vascular Fraction can be harmful
Expanded MESENCHYMAL STEM CELLS (MSCS) offer a highly purified, potent, and safe form of regenerative support in a wide range of chronic and inflammatory conditions. By contrast, STROMAL VASCULAR FRACTION (SVF) – a heterogeneous, minimally processed mixture extracted from adipose tissue – may actually worsen certain conditions due to its uncontrolled cellular composition. When it comes to regenerative medicine, not all cell therapies are the same. Many clinics offer stromal vascular fraction (SVF) as a quick solution—but what they don’t tell you is that SVF contains a large number of inflammatory cells that may actually worsen your condition.
In contrast, expanded Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) provide a targeted, purified, and scientifically validated supportive therapy with anti-inflammatory and regenerative effects.
The Stem Cell Source
Mesenchymal stem cells are the same regardless of whether they are derived from Adipose Tissue or Umbilical Cord Tissue. The only difference lies in their biological age, which reflects the age of the tissue of origin.

Adipose Tissue Derived Stem Cells
The treatment requires a fat collection, stem cell extraction, and expansion. The entire process takes approximately 2–3 weeks.(*)
Umbilical Cord Tissue derived Stem Cells
The treatment does not require fat harvesting and can be performed within 2–3 days of the request.
(*) Therefore, from the moment of fat harvesting, a waiting period of 2–3 weeks is necessary before the treatment can be performed.
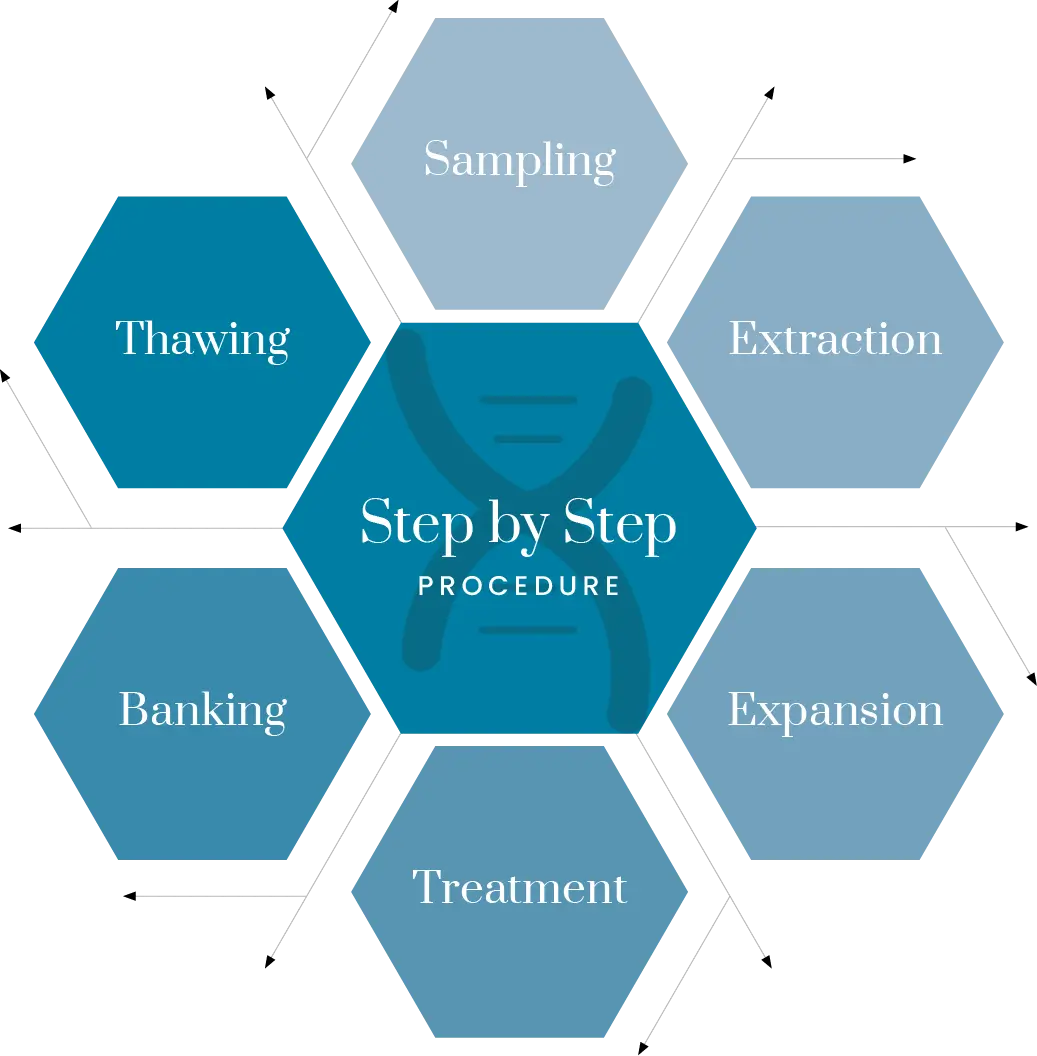
Let’s clarify with accurate information:
Stem Cells obtained from a fat sample require at least two weeks of processing before they can be used; otherwise, the treatment is ineffective and potentially harmful:
- Fat that is harvested and manipulated for use in the same session is both useless and harmful.
- There are no Stem Cells in the blood, so treatments claiming to use stem cells extracted from blood are not scientifically valid. The Stem Cells used to treat hematological diseases are found in the bone marrow, not in the blood.
- The hematopoietic stem cells found in umbilical cord blood are useful for treating blood disorders, but not for counteracting the aging processes of the human body
Ready to Take the Next Step?
Your journey to better health starts with a simple conversation
Our team of medical experts and dedicated patient coordinators is here to guide you every step of the way. From your initial consultation to post-treatment follow-up, we provide personalized support tailored to your unique needs. Schedule a free consultation today and discover how our advanced treatments can help you achieve your health goals.
