Restoring ovarian health and hormonal balance through regenerative stem cell therapy.
Premature Ovarian Failure
Struggling with the challenges of Premature Ovarian Failure? We have a natural, effective, and non-invasive solution.
Recent advances in Regenerative Medicine have identified expanded Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) as a promising treatment to restore ovarian function in women with POF.
Expanded Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) represent a paradigm shift in Reproductive Medicine: From managing decline to restoring function.
For women seeking a natural, effective, and non-invasive solution to Premature Ovarian Failure, this is the Gold Standard treatment option – superior to anything currently available on the market. Expanded Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) are now emerging as the most advanced and effective treatment, with the unique ability to restore ovarian health from within.
What is Premature Ovarian Failure (POF)?
Premature Ovarian Failure (POF) – also known as Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI) – is a condition in which the ovaries stop functioning normally before the age of 40. Unlike natural menopause, which typically occurs between ages 45 and 55, POF results in the early loss of fertility, irregular or absent menstrual cycles, and a significant decline in estrogen levels at a young age.

SYMPTOMS
- Irregular or missed periods (amenorrhea)
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Vaginal dryness and low libido
- Mood swings, depression, or anxiety
- Difficulty conceiving (infertility)
- Fatigue and difficulty concentrating
- Decreased bone density

MAIN CAUSES
- Genetic abnormalities (such as Turner Syndrome or Fragile X premutation)
- Autoimmune disorders
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy for cancer
- Environmental toxins and lifestyle factors
- Infectious diseases (such as mumps oophoritis)
- Idiopathic (unknown origin), in many cases
Physiological Basis
Premature Ovarian Failure occurs when the ovaries lose their normal function before the age of 40. In healthy ovaries, a complex interaction between follicular cells, granulosa cells, and hormonal signaling (primarily FSH and LH) supports folliculogenesis, estrogen production, and ovulation. In POF, this physiological balance is disrupted due to:
- Depletion or dysfunction of ovarian follicles
- Increased apoptosis of granulosa cell
- Reduced vascularization and oxygenation of ovarian tissue
- Chronic inflammation or autoimmune reactions
- Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
- Depletion or dysfunction of ovarian follicles
- Increased apoptosis of granulosa cell
- Reduced vascularization and oxygenation of ovarian tissue
- Chronic inflammation or autoimmune reactions
- Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
These alterations lead to hypoestrogenism, irregular ovulation, and often irreversible infertility. In many cases, the ovarian reserve is not completely depleted, but the microenvironment is too damaged to support proper follicular maturation.
Physical Consequences
- Osteoporosis and increased risk of bone fractures
- Cardiovascular disease due to low estrogen levels
- Accelerated aging of skin and tissues
- Weight gain and metabolic changes
Psychological and Emotional
Consequences
- Loss of identity or femininity
- Anxiety and depression
- Emotional distress from infertility
- Strained relationships and decreased quality of life
The Stem Cells Treatment: Minimally Invasive Procedure
For patients suffering from Peyronie’s disease the combined mesenchymal stem cell and collagenase treatment represents a state-of-the-art solution. Here’s why this therapy is considered by many experts as a “gold standard”approach moving forward:
- Regenerating damaged ovarian tissue
- Stimulating angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels)
- Modulating the immune response, reducing chronic inflammation
- Secreting growth factors and cytokines that enhance follicular survival and activation
- Inhibiting apoptosis of granulosa and stromal cells
- Improving mitochondrial function and reducing oxidative damage
At the forefront of innovative treatment, expanded MSCs are delivered directly into the ovaries through a minimally invasive intravaginal injection, guided by ultrasound for precision and safety. This technique ensures that the regenerative cells reach the ovarian stroma, where they can interact directly with dormant or damaged follicles to promote local repair and reactivate natural hormone production and ovulation in some cases.
Stem Cells is the Gold Standard
Expanded MSCs represent a paradigm shift in reproductive medicine: from managing decline to restoring function. For women seeking a natural, effective, and non-invasive solution to Premature Ovarian Failure, this is the Gold Standard treatment option – superior to anything currently available on the market.
Expanded Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) are now emerging as the most advanced and effective treatment for Premature Ovarian Failure, with the unique ability to restore ovarian health from within. why is superior:
The Stem Cell Source
Mesenchymal stem cells are the same regardless of whether they are derived from Adipose Tissue or Umbilical Cord Tissue. The only difference lies in their biological age, which reflects the age of the tissue of origin.

Adipose Tissue Derived Stem Cells
The treatment requires a fat collection, stem cell extraction, and expansion. The entire process takes approximately 2–3 weeks.(*)
Umbilical Cord Tissue derived Stem Cells
The treatment does not require fat harvesting and can be performed within 2–3 days of the request.
(*) Therefore, from the moment of fat harvesting, a waiting period of 2–3 weeks is necessary before the treatment can be performed.
Let’s clarify with accurate information:
Stem Cells obtained from a fat sample require at least two weeks of processing before they can be used; otherwise, the treatment is ineffective and potentially harmful:
- Fat that is harvested and manipulated for use in the same session is both useless and harmful.
- There are no Stem Cells in the blood, so treatments claiming to use stem cells extracted from blood are not scientifically valid. The Stem Cells used to treat hematological diseases are found in the bone marrow, not in the blood.
- The hematopoietic stem cells found in umbilical cord blood are useful for treating blood disorders, but not for counteracting the aging processes of the human body
Expected Timeline Of Results
Clinical and preclinical studies show:
- Menstrual cycle restoration may occur within 2 to 6 months post-treatment
- Hormone improvements—lowered FSH and raised estrogen and AMH levels—are typically seen within 1 to 3 months, sustained thereafter
- Follicular development and ovulation: increased antral, dominant, and mature follicles have been observed after 3–4 months
- Pregnancies in treated women (case reports) occurred between 6 and 12 months, although evidence is still limited to small cohortse.
Number of Treatments Needed:
- The majority of studies report a single injection may be sufficient to trigger ovarian activity and hormonal improvement.
- In cases where response is limited, a second injection after 3–6 months may be considered, guided by hormone levels and ultrasound findings
- Long-term follow-up studies are
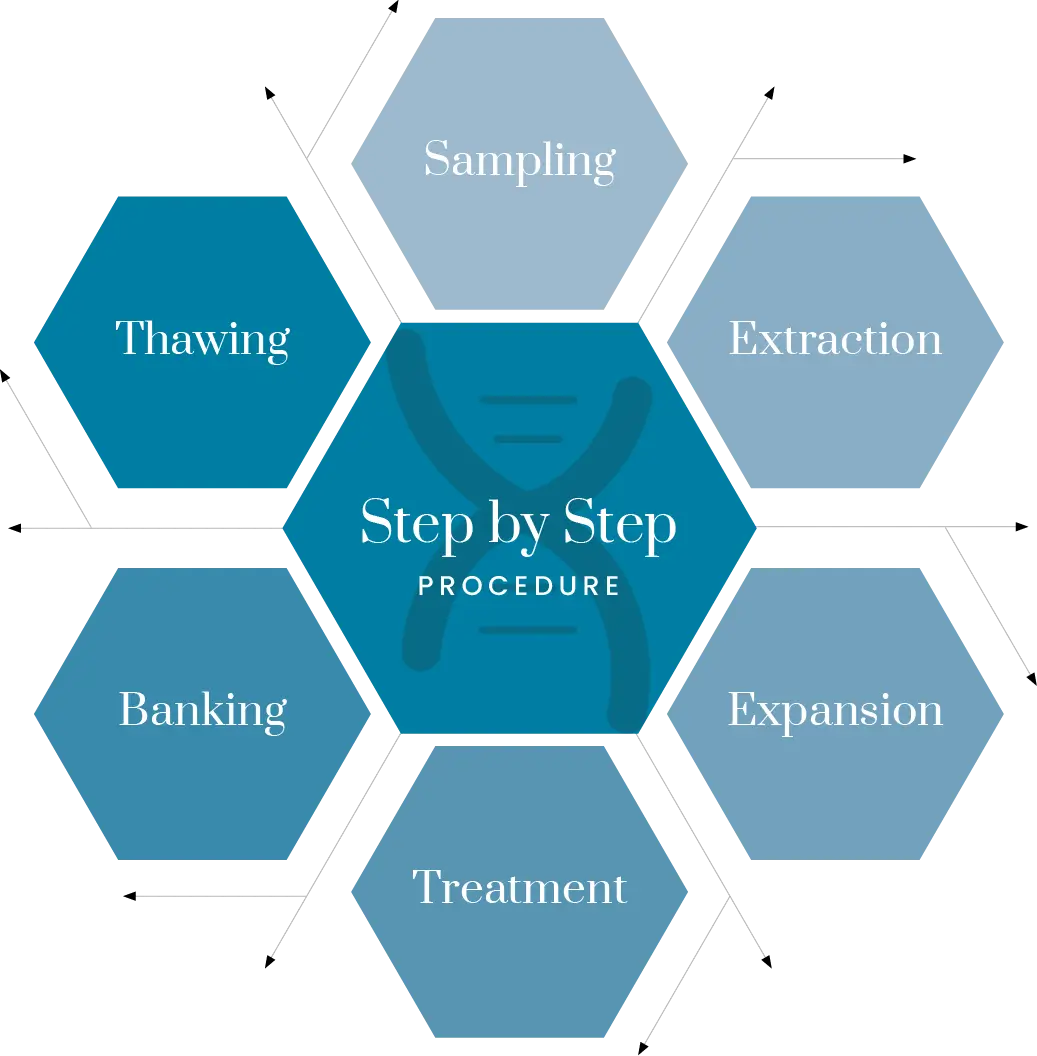
A simple Step-by-Step Procedure
From diagnosis to recovery, each phase is performed under strict clinical standards, ensuring optimal conditions for ovarian tissue regeneration and hormonal restoration.
Step 1: Patient Evaluation and Diagnosis
Before treatment begins, a comprehensive evaluation is performed to: - Confirm diagnosis of Premature Ovarian Failure - Assess ovarian reserve (via AMH levels, FSH, LH, and ultrasound) - Review medical history and eligibility for MSC therapy
Step 2: Stem Cell Preparation
- Mesenchymal stem cells are obtained from a biocompatible source (usually the patient’s own tissue or umbilical cord-derived allogenic MSCs) - Cells are isolated, purified, and expanded under Bioscience Institute GMP-certified laboratory - conditions to achieve optimal therapeutic concentration
Step 3: Scheduling the Procedure
- The treatment is performed in an outpatient setting - No general anesthesia or hospitalization is required - The procedure takes approximately 20–30 minutes
Step 4: Intravaginal Ovarian Injection
- The MSCs are injected directly into the ovaries using a transvaginal ultrasound-guided needle - This approach ensures precise, targeted delivery to the ovarian cortex, where dormant follicles and stromal tissue can benefit from the regenerative effect - The procedure is non-invasive, painless, and performed without incisions
Step 5: Recovery and Follow-Up
- Patients can resume normal activity within 24 hours
- Follow-up visits include hormonal profiling and ultrasound scans to monitor signs of ovarian reactivation
- In some cases, menstrual cycles may resume within a few weeks to months
The Unique Procedure:
- No surgery, no scars, no general anesthesia
- High-precision targeting of ovarian tissue
- Real potential to restore natural hormone production and fertility
- Zero downtime and minimal discomfort
Why Patient Selection Matters
Expanded MSC therapy is most effective when there is still some functional ovarian tissue present. Women with partial follicular function or residual vascularity tend to respond better than those with complete ovarian failure or fibrosis. Personalized assessment increases the chances of menstrual cycle recovery, hormonal improvement, and potential fertility restoration.
Who Is Eligible?
Not all women with Premature Ovarian Failure (POF), also known as Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI), are automatically eligible for regenerative treatment using expanded Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). Proper patient selection is critical to maximize success rates and ensure safety. Here are the general eligibility requirements:
INCLUSION CRITERIA
|
You may be considered a good candidate for MSC therapy if you meet most of the following conditions:
|
EXCLUSION CRITERIA
|
You may be considered a good candidate for MSC therapy if you meet most of the following conditions:
|
PRE-TREATMENT TESTING CHECKLIST
|
To determine eligibility, patients typically undergo
|
In-depth Information
Would you like to explore further or learn more? Access comprehensive explanations by expanding the sections below.
About Conventional Treatments and their Limitations
Oral Medications (e.g., Viagra, Cialis, Levitra)
How they work: Increase blood flow to the penis
Limitations: Do not address the root cause of ED, cause side effects and less effective in men with diabetes or severe vascular problems.
Penile Injections (e.g., Alprostadil)
How they work: Directly stimulate an erection by relaxing smooth muscle.
Limitations: Invasive and uncomfortable, side effects, temporary solution
Vacuum Erection Devices (Pumps)
How they work: Create a vacuum to draw blood into the penis.
Limitations: Unnatural or mechanical and erection quality insufficient for penetration.
Shockwave therapy
How they work: is a natural option for some men with early-stage ED—especially when blood flow is the main issue.
Limitations: it’s not a cure, and results are not permanent or predictable.
Summary of Limitations of Conventional Treatments
- Most treatments offer temporary relief, not a cure.
- They do not restore natural function or regenerate damaged tissue.
- Some require repeated use, planning, or surgery.
- Effectiveness may decrease over time or with underlying health conditions.
Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) VS Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC)
In the regenerative medicine landscape, many providers offer therapies labeled as “Stem Cell treatments” that utilize Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF)—a heterogeneous mix of cells extracted from adipose tissue. While SVF contains some Stem Cells, it also includes various other cell types, leading to variability in treatment outcomes.
At our Clinic, we prioritize precision and efficacy by exclusively using Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). These are meticulously isolated and expanded in controlled laboratory settings, ensuring a pure, potent, and standardized cell population. This approach enhances the therapeutic potential and consistency of our treatments.
Ready to Take the Next Step?
Your journey to better health starts with a simple conversation
Our team of medical experts and dedicated patient coordinators is here to guide you every step of the way. From your initial consultation to post-treatment follow-up, we provide personalized support tailored to your unique needs. Schedule a free consultation today and discover how our advanced treatments can help you achieve your health goals.
