Follow Bioscience Institute

The G-test is a non-invasive prenatal analysis for screening fetal chromosomal diseases.
From a maternal blood sample, important information on the health of the fetus is obtained, without compromising the pregnancy in any way.
Thanks to the next generation sequencing technology (Next Generation Sequencing) and the use of specific proprietary calculation algorithms it is possible to sequence the fragments of the DNA present in the maternal plasma to attribute its belonging to a specific chromosome, thus evaluating aneuploidies and chromosomal anomalies structural.
HOW DOES IT WORK
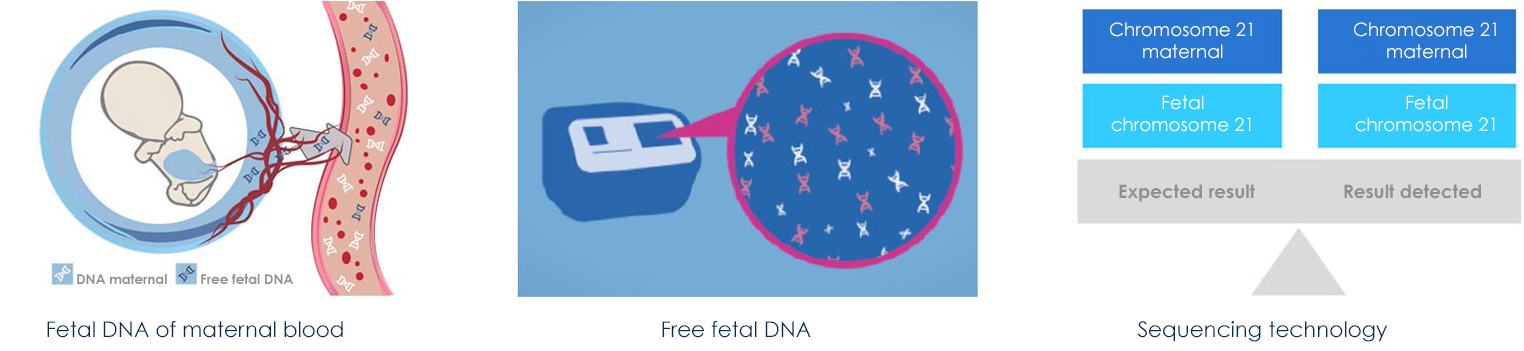
Cell free fetal DNA from maternal blood
During the first weeks of pregnancy, the embryo is fed by a group of cells (trophoblast) that will give rise to the placenta. Some of these cells will "break" naturally and will pour into their mother's bloodstream the DNA contained in them, in the form of fragments, going to make up what is called free fetal DNA.
Sequencing technology
The new generation sequencing (NGS) allows to order all the fragments of free DNA belonging to a specific chromosome and to compare them quantitatively with those normally present in a healthy individual to define the risk (high or low) that the fetus may be affected by chromosomal anomalies object of the test.

